[84] Lab Chip, 19, 9, 1665-1675, (2019)
Immature dendritic cells navigate microscopic mazes to find tumor cells
Eujin Um,ab Jung Min Oh,a Juhee Park,a Taegeun Song,c Tae-Eon Kim,a Yongjun Choi,ab Changsik Shin,a Diana Kolygina,a Jae-Hyung Jeon,c Bartosz A. Grzybowski*ab and Yoon-Kyoung Cho*ab
The challenge lies in understanding the recruitment of immune cells to the tumor site with the contradictory outcomes: tumor reduction or progression. The movement of immature dendritic cells, which navigate and sample the environment before activating the immune response, is random by nature, and recognizing the effective chemotactic cues towards cancer among a myriad of cytokines present in the surroundings is finding a needle in a haystack. In this paper, we find imposing physical constraints in the cell migration tracks in the geometry and dimensions modulates the directional persistence of dendritic cells. A delicate balance between chemotactic cues and the physical confinements reveals subtle chemotactic differences of dendritic cells in cancer vs. normal cell surroundings even inside a complex maze.
[83] ACS Nano, 13, 3, 3714-3722, (2019)
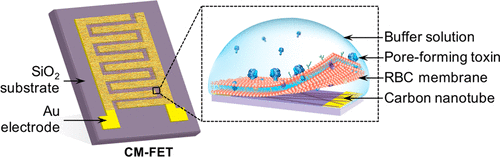
Biomembrane-modified field effect transistors for sensitive and quantitative detection of biological toxins and pathogens
Hua Gong, Fang Chen, Zhenlong Huang, Yue Gu, Qiangzhe Zhang, Yijie Chen, Yue Zhang, Jia Zhuang, Yoon-Kyoung Cho, Ronnie H. Fang, Weiwei Gao, Sheng Xu*, and Liangfang Zhang*
Herein, we report a cell-membrane-modified field effect transistor (FET) as a function-based nanosensor for the detection and quantitative measurement of numerous toxins and biological samples. By coating carbon nanotube FETs with natural red blood cell membranes, the resulting biomimetic nanosensor can selectively interact with and absorb broad-spectrum hemolytic toxins regardless of their molecular structures. Toxin–biomembrane interactions alter the local charge distribution at the FET surface in an ultrasensitive and concentration-dependent manner, resulting in a detection limit down to the femtomolar (fM) range.
[82] Theranostics, 9, 7, 1851-1863, (2019)
Fully automated, label-free isolation of extracellular vesicles from whole blood for cancer diagnosis and monitoring
Vijaya Sunkara+, Chi-Ju Kim+, Juhee Park, Hyun-Kyung Woo, Dongyoung Kim, Hong Koo Ha, Mi-Hyun Kim, Youlim Son, Jae-Ryong Kim, Yoon-Kyoung Cho*
Lab-on-a-disc equipped with sequential nanofiltration is presented for fully automated, rapid, label-free EV enrichment with high yield and purity starting from whole blood or plasma for cancer diagnosis and monitoring.
[81] Biomaterials science, 7, 4, 1393-1398, (2019)
Biologically-active unilamellar vesicles from red blood cells
Hyun-Sook Jang, Yoon-Kyoung Cho, and Steve Granick*
We demonstrate a method to prepare giant unilamellar vesicles (GUVs) with biologically-active protein activity, by mixing erythrocyte (red blood cell) membrane extract with phospholipids and growing their mixture in a porous hydrogel matrix. This presents a pathway to retain protein biological activity without prior isolation and purification of the protein.
[80] Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 127, 15, 50-56, (2019)
Universal Method for Direct Bioconjugation of Electrode Surfaces by Fast Enzymatic Polymerization
Sumit Kumar, Al-Monsur Jiaul Haque, Jonathan Sabaté del Río, Shreedhar Gautam, Yoon-Kyoung Cho*
This HRP-catalyzed polymerization of TA and p(TA)-mediated surface modification method can provide a simple and new framework to construct multifunctional platforms for covalent attachment of biomolecules and development of sensitive electrochemical sensing devices
[79] ACS Catalysis, 9, 2, 977–990, (2019)
Plasmonically Coupled Nanoreactors for NIR-Light-Mediated Remote Stimulation of Catalysis in Living Cells
Amit Kumar, Sumit Kumar, Nitee Kumari, Seon Hee Lee, Jay Han, Issac Michael, Yoon-Kyoung Cho*, In Su Lee*
Artificial nanoreactors that can facilitate catalysis in living systems on-demand with the aid of remotely operable and biocompatible energy-source, are needed to leverage the chemical diversity and expediency of advanced chemical synthesis in biology and medicine. Here, we designed and synthesized plasmonically-integrated nanoreactors (PINERs) with highly tunable structure and NIR-light-induced synergistic function for efficiently promoting unnatural catalytic reactions inside living cells.
[78] Lab Chip, 19, 1, 87-97, (2019)
Urine-based liquid biopsy: non-invasive and sensitive AR-V7 detection in urinary EVs from patients with prostate cancer
Hyun-Kyung Woo+, Juhee Park+, Ja Yoon Ku, Chan Ho Lee, Vijaya Sunkara, Hong Koo Ha* and Yoon-Kyoung Cho*
Androgen receptor splice variant 7 (AR-V7) is associated with castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) and resistance to anti-androgen therapy. Herein, we suggest a practical and non-invasive liquid biopsy method for analysis of AR-V7 in the RNA of urine-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) without the need for blood withdrawal. Higher AR-V7 and lower AR-FL expression were detected in urine-derived EVs from 14 patients with CRPC than in those from 22 patients with hormone-sensitive prostate cancer. This study is the first to report that RNA of urine-derived EVs is a reliable source for AR-V7 expression analysis. The proposed method for quantifying AR-V7 in urinary EVs prepared by a lab-on-a-disc is, therefore, a simple and promising approach to liquid biopsy with great potential for therapeutic impact on prostate cancer.
[77] Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 34, 3, 552-560, (2018)
Circulating tumor cells detected using fluid‐assisted separation technique in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Mun Ki Choi, Gwang Ha Kim*, Hoseok I, Su Jin Park, Moon Won Lee, Bong Eun Lee, Do Youn Park, Yoon‐Kyoung Cho
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is one of the aggressive gastrointestinal tract cancers. Detection of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) in peripheral blood from patients with various malignancies has been reported to have diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic implications. We aimed to evaluate CTCs in patients with ESCC and assess the clinical significance of CTCs in the early diagnosis of ESCC.
[76] PNAS, 115, 46, E10812-E10821, (2018)
Catalytic enzymes are active matter
Ah-Young Jee, Yoon-Kyoung Cho, Steve Granick, and Tsvi Tlusty
Catalysis and mobility of reactants in fluid are normally thought to be decoupled. Violating this classical paradigm, this paper presents the catalyst laws of motion. Comparing experimental data to the theory presented here, we conclude that part of the free energy released by chemical reaction is channeled into driving catalysts to execute wormlike trajectories by piconewton forces performing work of a few kBT against fluid viscosity, where the rotational diffusion rate dictates the trajectory persistence length. This active motion agitates the fluid medium and produces antichemotaxis, the migration of catalyst down the gradient of the reactant concentration. Alternative explanations of enhanced catalyst mobility are examined critically.
[75] J. Am. Chem. Soc., 140, 45,1 5176–15180, (2018)
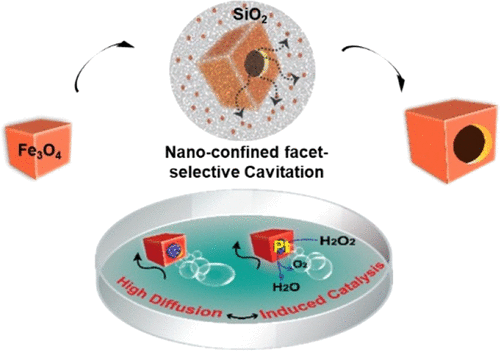
Monofacet-Selective Cavitation within Solid-State Silica-Nanoconfinement toward Janus Iron Oxide Nanocube
Sunyi Lee, Nitee Kumari, Ki-Wan Jeon, Amit Kumar, Sumit Kumar, Jung Hun Koo, Jihwan Lee, Yoon-Kyoung Cho, and In Su Lee*
The Janus-type concave iron oxide nanocube was further functionalized with the controllable density of catalytic Pt-nanocrystals exclusively on concave sites and utilized as a highly diffusive catalytic Janus nano-swimmer for the efficient degradation of pollutant-dyes in water. The strategy is based on a novel heat-induced nanospace-confined domino-type migration of Fe2+ions from the SiO2–Fe3O4 interface toward the surrounding silica shell and concomitant self-limiting nanoscale phase-transition to the Fe-silicate form.
[74] ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 10, 40, 33839-33846, (2018)
Surface Engineered Paper Hanging Drop Chip for 3D Spheroid Culture and Analysis.
Issac Michael, Sumit Kumar, Jung Min Oh, Dongyoung Kim, Junyoung Kim, Yoon-Kyoung Cho*
We demonstrated hanging drop three-dimensional (3D) spheroid culture and in-site analysis, including drug testing, time-dependent detection of secreted protein, and fluorescence staining without disturbing the spheroids. This single hanging drop system can also be extended to a networked hanging drop chip to mimic in vivo microphysiology by combining with wax-patterned microfluidic channels, where well-to-well interaction can be accurately controlled in a passive manner. Our method demonstrates a future possibility for paper as a low cost, high-throughput 3D spheroid-based “body-on-a-chip” platform material.
The Korean Journal of Helicobacter and Upper Gastrointestinal Research 18, 3, 157-161, (2018)
Current Methods of Circulating Tumor Cell Detection
Minji Lee and Yoon-Kyoung Cho*
We provide an overview of the current CTC isolation methods and examples of their potential application for early diagnosis, prognosis, treatment monitoring, and prediction of resistance to cancer therapy. Furthermore, the challenges that remain to be addressed before such tools are implemented for routine use in clinical settings are discussed.
[73] Acta Biomaterialia, 77, 311-321, (2018)
Substrate curvature affects the shape, orientation, and polarization of renal epithelial cells
Sun-Min Yu, Jung Min Oh, Junwon Lee, Whaseon Lee-Kwon, Woonggyu Jung, François Amblard, Steve Granick, Yoon-Kyoung Cho*
Our study suggests curvature be an important guiding principle for advanced tissue model developments, and that curved and geometrically ambiguous substrate can modulate the cellular morphology and phenotype.
[72] Small 2018, 14, 34, (2008)
Cloaked Exosomes: Biocompatible, Durable, and Degradable Encapsulation
Sumit Kumar, Issac J. Michael, Juhee Park, Steve Granick, Yoon-Kyoung Cho*
Exosomes are protected against external stress, especially UV irradiation and elevated temperature, by a protective nanolayer of ferric ion and tannic acid. On-demand chemical degradation and further surface functionalization capabilities on exosomes open up new applications beyond their native functions.
[71] RSC Advances, 8, 35, 19651-19658, (2018)
Non-lithographic nanofluidic channels with precisely controlled circular cross sections
Yang-Seok Park, Jung Min Oh and Yoon-Kyoung Cho*
we report the application of a nanofiber printed using a near-field electrospinning method as a sacrificial mold for the preparation of polydimethylsiloxane nanochannels with circular cross sections
[70] Lab Chip, 18, 9, 1320-1329, (2018)
Fully automated, on-site isolation of cfDNA from whole blood for cancer therapy monitoring
Chi-Ju Kim, Juhee Park, Vijaya Sunkara, Tae-Hyeong Kim, Yongjin Lee, Kyusang Lee, Mi-Hyun Kim and Yoon-Kyoung Cho*
Fully integrated lab-on-a-disc for cfDNA isolation allows real-time monitoring of tumor mutation status during targeted therapy.
[69] Micromachines, 9, 3, 100, (2018)
Liquid Biopsy in Lung Cancer: Clinical Applications of Circulating Biomarkers (CTCs and ctDNA)
Minji Lim+, Chi-Ju Kim+,Vijaya Sunkara , Mi-Hyun Kim and Yoon-Kyoung Cho*
In this review, we examined the clinical significance and uniqueness of CTCs and ctDNA from NSCLC patients, isolation and detection methods developed to analyze each type of circulating biomarker, and examples of clinical studies of potential applications for early diagnosis, prognosis, treatment monitoring, and prediction of resistance to therapy. We also discuss challenges that remain to be addressed before such tools are implemented for routine use in clinical settings.
[68] PNAS, 115, 1, 14-18, (2018)
Enzyme leaps fuel antichemotaxis
Ah-Young Jee, Sandipan Dutta, Yoon-Kyoung Cho, Tsvi Tlusty, and Steve Granick*
Challenging the traditional view that enzyme kinetics are only a matter of catalyzing chemical reactions, there is mounting evidence that the enzyme catalysis enhances enzyme mobility. This is significant to programming spatio-temporal patterns of molecular response to chemical stimulus, which is common to living matter as well as to significant chemical technology. This paper shows that the enhanced diffusivity of enzymes is a “run-and-tumble” process analogous to that performed by swimming microorganisms, executed in this situation by molecules that lack the decision-making machinery of microorganisms. The result is that enzymes display “antichemotaxis” when they turn over substrate; they migrate in the direction of lesser reactant concentratio
[67] Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 256, 310-317, (2018)
Centrifugal Microfluidic System for a Fully Automated N-fold Serial Dilution
Tae-Hyeong Kim, Chi-Ju Kim, Yubin Kim, Yoon-Kyoung Cho*
N-fold serial dilution with a choice of N = 2, 5, 10 is fully integrated and automated on a centrifugal microfluidic system. Individually addressable, reversible diaphragm valves are utilized to enable the automatic control of the fluidic transfer and metering of the liquid.
Nobel Symposium 162 - Microfluidics, Stockholm, Sweden; arXiv:1712.08369 [physics.flu-dyn]
Centrifugal Microfluidics for Biomedical Applications
Yoon-Kyoung Cho
The Nobel Foundation's Symposium programme was initiated in 1965 and since then over 160 symposia have taken place. With the Nobel symposium summarized in this proceedings volume, we had the ambition to cover the past, current and future developments of microfluidics; a highly challenging task as there are many excellent researchers in this area and only thirty slots in the program. We tried to cover the early breakthrough contributions to the field, important developments over the years and applications of microfluidics that now propagate in vastly different directions both as industrial components or processes and as tools and methods supporting fundamental research